-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Ranking
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Student Visas
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Exams
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Exams
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Online Courses
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Animation Courses
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Exams
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


All Questions
The strength of an aqueous NaOH solution is most accurately determined by titrating:
(Note: consider that an appropriate indicator is used)
Option: 1 Aq.NaOH in a pipette and aqueous oxalic acid in a burette
Option: 2 Aq.NaOH in a volumetric flask and concentrated in a conical flask
Option: 3 Aq.NaOH in a burette and concentrated in a conical flask
Option: 4 Aq.NaOH in a burette and aqueous oxalic acid in a conical flask
As we have learnt,
To calculate the strength of NaOH, it is titrated against oxalic acid. For this purpose, NaOH is kept in a burette and oxalic acid in a conical flask.
Therefore, Option(4) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)Reaction of an inorganic sulphite X with dilute 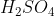 generates compound Y.Reaction of Y with
generates compound Y.Reaction of Y with 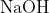 gives X. Further, the reaction of X with Y and water affords compound Z. Y and Z, respectively, are :
gives X. Further, the reaction of X with Y and water affords compound Z. Y and Z, respectively, are :
Option: 1 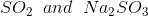
Option: 2 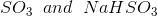
Option: 3 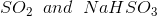
Option: 4 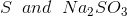
The reaction will be-

So, Y and Z, respectively, are
Therefore, the correct option is (3).
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

If you spill a chemical toilet cleaning liquid on your hand, your first aid would be:
Option: 1 aqueous NH3
Option: 2 gaseous NaHCO3
Option: 3 aqueous NaOH
Option: 4 Vinegar
Chemical toilet cleaning liquid contains acid and hence the first aid would be a weak base like NaHCO3.
Therefore, Option(2) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)The addition of dilute  salt solution will give :
salt solution will give :
Option: 1 Precipitate of 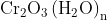
Option: 2 Precipitate of 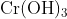
Option: 3 Precipitate of ![\left[\mathrm{Cr}(\mathrm{OH})_{6}\right]^{3-}](https://learn.careers360.com/latex-image/?%5Cleft%5B%5Cmathrm%7BCr%7D%28%5Cmathrm%7BOH%7D%29_%7B6%7D%5Cright%5D%5E%7B3-%7D)
Option: 4 A solution of ![\left[\mathrm{Cr}(\mathrm{OH})_{4}\right]^{-}](https://learn.careers360.com/latex-image/?%5Cleft%5B%5Cmathrm%7BCr%7D%28%5Cmathrm%7BOH%7D%29_%7B4%7D%5Cright%5D%5E%7B-%7D)
Addition of dilute to a salt solution of
will lead to the formation of a precipitate of hydrated chromium (III) oxide.
Hence, the correct answer is option (1)
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE
Acidic ferric chloride solution on treatment with excess of potassium ferrocyanide gives a Prussian blue coloured colloidal species. It is :
Option: 1 ![\mathrm{HFe}\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_{6}\right]](https://learn.careers360.com/latex-image/?%5Cmathrm%7BHFe%7D%5Cleft%5B%5Cmathrm%7BFe%7D%28%5Cmathrm%7BCN%7D%29_%7B6%7D%5Cright%5D)
Option: 2 ![\mathrm{K}_{5} \mathrm{Fe}\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_{6}\right]_{2}](https://learn.careers360.com/latex-image/?%5Cmathrm%7BK%7D_%7B5%7D%20%5Cmathrm%7BFe%7D%5Cleft%5B%5Cmathrm%7BFe%7D%28%5Cmathrm%7BCN%7D%29_%7B6%7D%5Cright%5D_%7B2%7D)
Option: 3 ![\mathrm{Fe}_{4}\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_{6}\right]_{3}](https://learn.careers360.com/latex-image/?%5Cmathrm%7BFe%7D_%7B4%7D%5Cleft%5B%5Cmathrm%7BFe%7D%28%5Cmathrm%7BCN%7D%29_%7B6%7D%5Cright%5D_%7B3%7D)
Option: 4 ![\mathrm{KFe}\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_{6}\right]](https://learn.careers360.com/latex-image/?%5Cmathrm%7BKFe%7D%5Cleft%5B%5Cmathrm%7BFe%7D%28%5Cmathrm%7BCN%7D%29_%7B6%7D%5Cright%5D)
ions react with excess of potassium ferrocyanide to form
.
The reaction is given below:
Hence,the correct answer is Option (4)
View Full Answer(1)Match List - I with List - II :
| List-I (Metal Ion) | List-II (Group in Qualitative analysis) |
| (i) Group - III | |
| (ii) Group - IIA | |
| (iii) Group - IV | |
| (iv) Group - IIB |
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
The correct match of basic radicalsand their groups in Qualitative analysis is given below
Hence the correct answer is option (1)
View Full Answer(1)NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
- Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score up to 100% marks
Consider the sulphides and
. Number of these sulphides soluble in
is_________.
The sulphide which are soluble in are
Sulphides insoluble in are
and
Hence, the correct answer is 4
View Full Answer(1)The potassium ferrocyanide solution gives a Prussian blue colour, when added to:
Option: 1 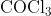
Option: 2 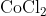
Option: 3 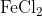
Option: 4 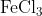
Prussian Blue is formed when reacts with ferric ions
Hence, the correct answer is option (4)
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

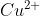 salt reacts with potassium iodide to give
salt reacts with potassium iodide to give
Option: 1 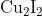
Option: 2 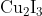
Option: 3 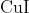
Option: 4 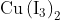
reacts with
to form precipitate of
.
is reduced to
while Iodide ions are oxidised to Iodine as shown below
The complexes with
to give tri iodide ions
which forms a reddish solution.
Hence, the correct answer is option (1).
View Full Answer(1)An inorganic Compound 'X' on treatment with concentrated produces brown fumes and gives dark brown ring with
in presence of concentrated
. Also Compound 'X' gives precipitate 'Y', when its solution in dilute HCl is treated with
gas. The precipitate 'Y' on treatment with concentrated
followed by excess of
further gives deep blue coloured solution, Compound 'X' is:
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
Acconding to the information given in the question
This confirms the presence of Nitrate ions as the acidic Radical.
The precipitation with in presence of dil. HCl tells us that the Basic radical is of Group (2).
Futher reaction of the precipitate with and excess
giving a blue solution confirms the presence of
ions
Hence, the correct answer is option (3)
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE


